Speed and Precision
Whether a machine is designed to assemble connectors, switches, sockets, electrical subcomponents, or harnesses, typical processes involve loading parts in the machine, inserting them within an assembly, dispensing and curing glue, labeling/printing/marking, crimping, inspecting/testing, screwing, rejecting, and unloading parts, with some other processes such as welding and cutting being common in the field.
Additional Advantages
The main challenge in electrical device and wiring harness manufacturing is managing floor space, as production areas are often crowded with operational machines or idle equipment for spare parts. Adjusting production batches daily is also crucial for meeting the varying demands of customers.

Smart Conveyance Goal
Smart Conveyance aims to reduce floor space while increasing flexibility, achieving similar or higher throughput at competitive prices compared to traditional systems.
Smart Manufacturing Solutions
SuperTrak CONVEYANCE™ delivers value by enabling complex motion at each process step, reducing the need for additional tooling and enabling more processes to occur at a single location.
Addressing Core Needs
With software controlling the motion of automation, carrying or adding multiple products on the same line becomes easier.
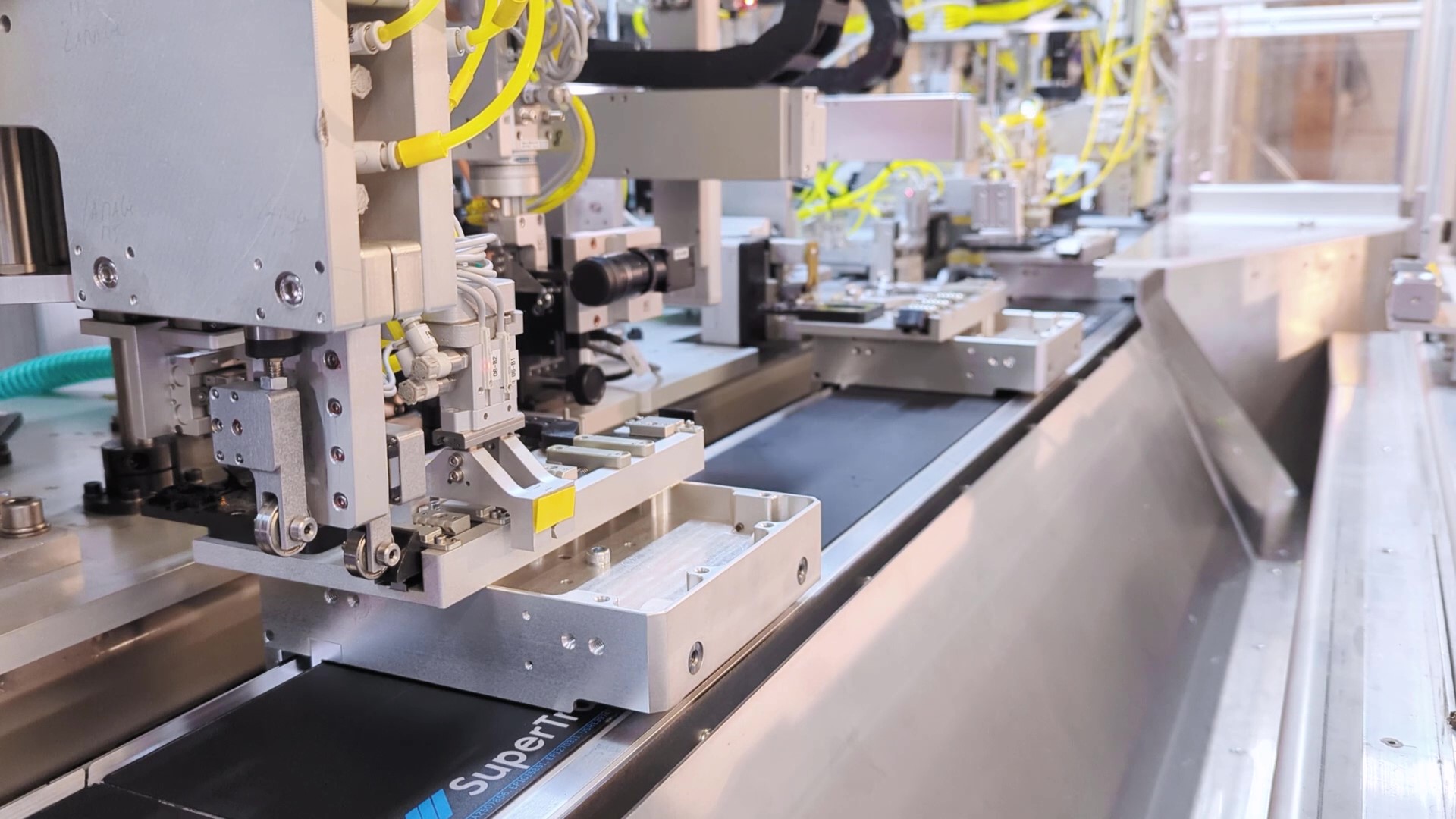
Wiring Harness Application
Larisys Industries successfully implemented an assembly machine based on a 4m SuperTrak VERTICAL10™ system for a wiring harness application. The final machine’s size, approximately half that of a standard conveyance solution, improved accessibility and maintenance.
“The SuperTrak technology is disruptive because of its speed, precision, compact design and capability to be easily configurable.”
Larisys Group
SuperTrak CONVEYANCE™ Users
Showcase Their Machines in Action:
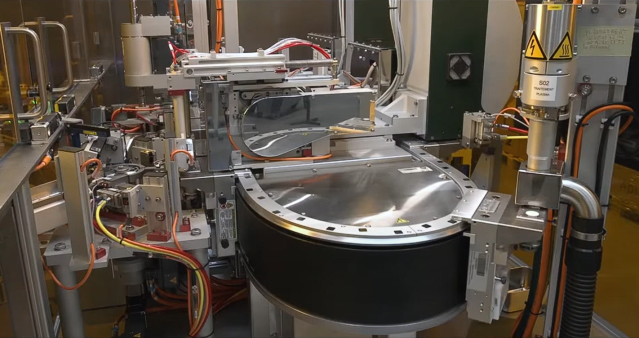
Customer Highlights
Simplify Design & Integration
“The key advantage of this magnetic track system is to convey linearly and very precisely the parts […]. Reliability, repeatability, high-speed transfers are also strong arguments for SuperTrak”
Neyret Group
(SuperTrak HORIZON10™ distributed by B&R™)

Customer Highlights
Assembly Processes
“Assembly processes are typically implemented using shuttle transport systems for workpiece transport, combined with our handling modules. Our goal is to achieve optimal production flow with minimal footprint.”
K&S Anlagenbau GmbH
(SuperTrak HORIZON10™ distributed by Bosch Rexroth™ under the name ActiveMover™)
Get Started with Smart Conveyance
Speak with a SuperTrak CONVEYANCE™ team member today to see how you can unlock your process’s potential by levering higher speed, increased precision, and independent shuttle control.
If you have an upcoming project, now is the time to start thinking about your conveyance system.

